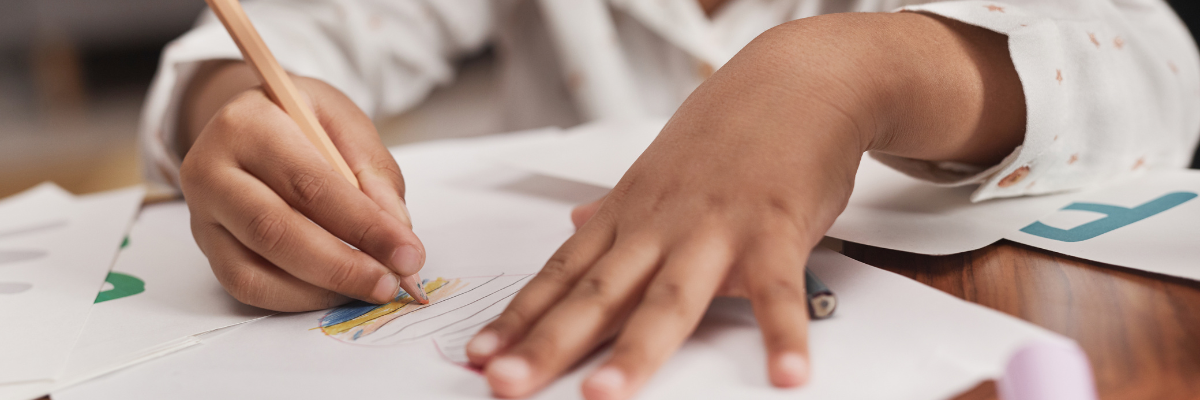
Fine motor skills are getting worse in kids today. More and more children struggle to hold pencils, use scissors, or even tie their shoes. According to a recent report from Art-K, 77% of teachers say that fine motor skills are harder for students now than just a few years ago. So, what’s causing this decline? And more importantly, what can parents do to help?
Carolina Therapy Connection specializes in helping children in Greenville, New Bern, Morehead City, and Goldsboro, NC, develop the skills they need to succeed. Our occupational therapy (OT) services focus on fine motor development, handwriting, coordination, and self-care skills to give kids confidence and independence.
Why Are Kids Losing Fine Motor Skills?
Experts point to several key reasons why fine motor skills are declining:
1. Too Much Screen Time
Instead of playing with toys, coloring, or building with blocks, many children spend hours swiping and tapping on screens. This doesn’t give their hands the same strength-building practice as traditional play.
2. Less Hands-On Learning
Many children aren’t getting enough time to practice holding crayons, cutting with scissors, or playing with small objects. Fewer opportunities for these activities can make school tasks much harder.
3. Not Enough Outdoor Play
Running, climbing, digging, and playing outside help strengthen a child’s hands and improve coordination. But many kids today spend less time outdoors, limiting natural muscle development.
4. Clothing and Snack Changes
Modern clothing and food packaging have made life easier but have also reduced everyday fine motor practice. Elastic waistbands replace buttons and zippers, Velcro shoes replace laces, and pre-packaged snacks mean kids don’t open containers or use utensils as much as before.
Simple Ways Parents Can Help at Home
The good news? You can help your child strengthen their fine motor skills with easy, fun activities at home! Here are simple, practical steps to get started:
1. Encourage Daily Fine Motor Play
Fine motor skills develop best through play. Try these activities:
- Play-Doh and Clay – Let kids roll, pinch, and shape clay to build hand strength.
- Puzzles and Bead Threading – These boost coordination and dexterity.
- Lacing Cards or Sewing Projects – Great for developing control and finger strength.
- Scissor Skills – Have kids cut paper, old magazines, or even straws for fun crafts.
2. Get Kids Involved in Everyday Tasks
Let your child help with activities that naturally build fine motor skills, such as:
- Cooking Together – Stirring, pouring, kneading dough, and peeling fruit strengthen hands.
- Self-Care Tasks – Encourage kids to button shirts, zip jackets, and tie shoelaces.
- Household Chores – Folding laundry, wiping tables, and opening containers all help build fine motor strength.
3. Limit Screen Time and Increase Hands-On Activities
Try implementing screen-free times, especially before and after school. Instead, encourage activities like:
- Drawing and Coloring – A fun way to develop pencil grip and hand control.
- Playing with Blocks and LEGOs – Helps strengthen little fingers and improve problem-solving skills.
- Outdoor Play – Let kids dig in the dirt, climb, and collect small objects like acorns or leaves.
4. Make Handwriting Practice Fun
If your child struggles with handwriting, avoid frustration by making it engaging and low-pressure:
- Use a Sand or Rice Tray – Have kids practice letters by tracing them with their fingers.
- Write on a Chalkboard or Whiteboard – This builds wrist and hand strength.
- Try Special Handwriting Tools – Use thicker pencils, grips, or markers for better control.
- Turn Writing into a Game – Write letters in shaving cream or use sidewalk chalk outside.
- Use Fun Sensory Feedback– Using all of your senses increases learning. Think smell, sounds, and textures.
How Carolina Therapy Connection Can Help
At Carolina Therapy Connection, our occupational therapists use fun, play-based techniques to improve fine motor skills. We help kids in Greenville, New Bern, Morehead City, and Goldsboro, NC with:
- Hand Strength Training – Using squeeze toys, tweezers, and resistance exercises.
- Coordination Development – Working on scissor use, handwriting, and using both hands together.
- Self-Care Skills – Teaching kids to tie shoes, button clothes, and use utensils confidently.
- Handwriting Support – Helping kids develop a firm pencil grip and letter formation skills.
When Should You Seek Help?
If your child:
- Struggles with holding a pencil or writing legibly
- Has trouble using scissors or fastening buttons
- Avoids activities that require hand coordination
- Seems behind peers in self-care tasks
… they may benefit from occupational therapy.
Contact us today at Carolina Therapy Connection to learn how our team can help your child build stronger hands and gain confidence in everyday tasks!