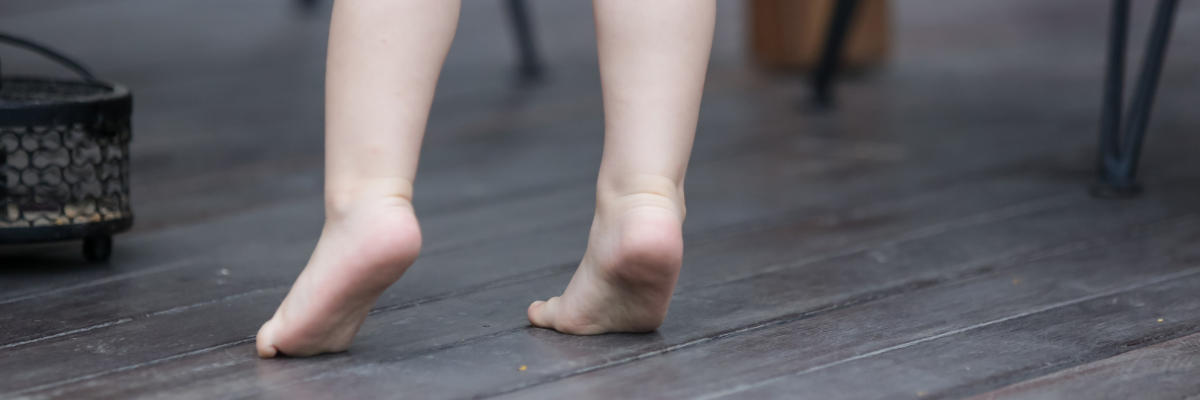
Toe walking means that a child is walking and standing on tiptoes, and their heels do not make contact with the ground. Walking up on their toes can be a normal occurrence in children aged three and under as they continue to develop their ability to walk. Beyond that age, without any definitive medical reason, it is considered idiopathic toe walking (walking on toes without a known cause).
Toe Walking Causes
To understand, what’s not so simple about toe walking is the why behind it. There are many possible reasons that children might develop this pattern:
Developmental phase: A child occasionally walking on the balls of their feet can be part of normal development. When children first begin walking, usually between 12-15 months of age, they often try different foot positions including walking up on their toes. However, it is expected that typically developing children will only walk on their toes occasionally.
Neurological concern:
- Sensory processing concerns: Children with sensory issues, including those on the Autism Spectrum related to the vestibular system, have a different awareness of their body position and feel stabilized during toe walking. The tactile system includes our sense of touch, pain, and temperature. Some studies conclude that children with differences in vestibular processing can also have tactile senses that exacerbate their toe walking. They may not like the feeling of the floor touching their feet, and toe walking minimizes this contact. Children seeking proprioceptive input toe walk because the gait prolongs stimulation of joint receptors and causes their muscles to tighten. The movement provides a calming input sensation for the child. (Williams 2010)
- Cerebral Palsy: The most common cause of toe walking in those with cerebral palsy is spasticity, which can cause stiffness and involuntary muscle contractions in calf muscles, keeping their heels from touching the ground. Over time, without proper stretching and bracing, these muscles can become shortened, making it challenging to achieve heel contact.
Idiopathic toe walking: Toe walking can occur because of an underlying anatomic or neuromuscular condition, but in most cases, toe walking is idiopathic without a discernible underlying cause. Idiopathic toe walking occurs in children between 3 and 7 years old and is more commonly seen in males than females. Idiopathic toe walking is not related to any specific diagnosis and can presenty of reasons, due to a variet including decreased stability and sensory involvement. For some families, toe walking may be a cosmetic concern, whereas it can cause pain or functional issues in other cases. (Ruzbarsky, Scher, & Dodwell, 2016)
Treatment
You may wonder how to stop toe-walking with your child. Therapeutic treatment depends on the cause, how strong of a habit it is, how tight the calf muscles have become, and what other changes have occurred in the child’s foot and ankle due to walking this way.
Treatment can include:
- Stretching: To improve muscle length, increase ankle mobility, and promote heel contact
- Orthoses: Ankle-foot orthotic worn to keep the foot at a 90-degree angle and promote heel contact
- *Turtle bracing: New bracing technique utilizing a removable, re-moldable, lightweight brace to achieve optimal ankle positioning, obtain and maintain ankle mobility, and promote heel contact
- Serial Castings: Hard cast used to obtain and maintain a 90-degree angle at the ankle joint for extended periods (1-2 weeks at a time)
- Night splints: Braces worn at night to keep the foot in a 90-degree angle and achieve prolonged stretch
- Botox injections are most commonly used with those dealing with spasticity; they weaken their calf muscles and make them easier to stretch and cast.
A careful history, clinical exam, and selective diagnostic testing can be used to differentiate between different types of toe walking and determine the most appropriate treatment for each child.
How Can Carolina Therapy Connection Help with Toe Walking?
Being evaluated by a Physical or Occupational Therapist can further help determine which treatment routes are appropriate for your child. Call us today at 252-341-9944 for a free screening!
By: Taylor Saunders