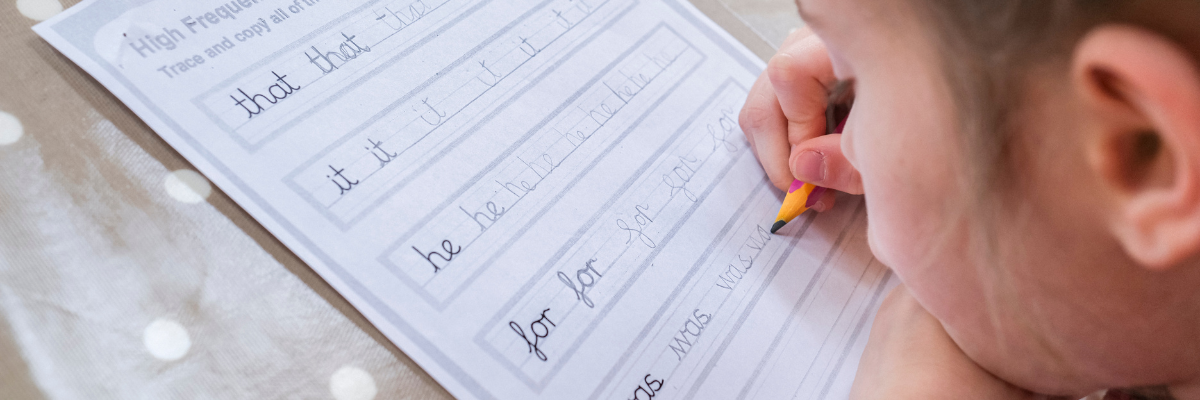Teaching kids handwriting is an essential skill that sets them up for success in school and beyond.
Here are some tips to make handwriting practice fun and effective for children:
Start with the Basics:
- Begin by teaching them how to hold a pencil properly. Make sure they grip it comfortably but firmly.
- Use Large Lines: Provide paper with large lines to help them understand the proportions of letters. You can find special handwritten papers with guidelines specifically for this purpose.
- Practice Letter Formation: Start with uppercase letters and then move on to lowercase. Demonstrate how each letter is formed and encourage them to mimic your movements.
- Repetition: Handwriting improves with practice. Encourage kids to practice writing letters and words regularly. You can make it more engaging by turning it into a game or challenge.
- Use Multisensory Approaches: Incorporate different senses into handwriting practice. For example, tracing letters in sand or shaving cream can provide tactile feedback that reinforces learning.
- Provide Positive Feedback: Praise their efforts and progress. Positive reinforcement can boost their confidence and motivation to continue practicing.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set achievable goals for improvement and celebrate their milestones along the way.
- Be Patient: Remember that learning handwriting takes time and patience. Encourage persistence and provide support when they feel frustrated.
Making handwriting practice fun for kids can encourage them to engage with the activity more eagerly when writing isn’t so easy. Here are some creative and fun ideas to make handwriting more fun:
- Write with Different Materials: Encourage kids to write on a chalkboard with different materials, such as colored pencils, gel pens, markers, or chalk.
- Rainbow Writing: Have kids trace over letters or words multiple times using different colored pencils or markers.
- Letter Hunt: Create a scavenger hunt where kids search for letters in books, magazines, or around the house. Once they find a letter, they can write it down!
- Write a Story: Encourage kids to write a short story or a letter to a friend or family member.
- Write on Unconventional Surfaces: Let kids write on unconventional surfaces such as a large whiteboard, a window with washable markers, or even with their fingers in sand or shaving cream.
- Handwriting Games: Incorporate games into handwriting practice, such as Hangman, Tic-Tac-Toe, or Bingo, using words or letters.
- Decorate Letters: After writing a letter or word, encourage kids to decorate it with doodles, stickers, or drawings related to the word.
- Write Secret Messages: Have kids write secret messages to each other using a white crayon on white paper. When they’re done writing, they can reveal the messages by painting over it with watercolors.
- Create Handwriting Challenges: Set up fun handwriting challenges such as writing the alphabet backward, writing with their non-dominant hand, or writing as neatly and as quickly as possible.
How can Carolina Therapy Connection help with kids’ handwriting skills?
If your kiddo is having difficulty with handwriting, an Occupational Therapist at CTC can help! Whether it be because your kiddo doesn’t attend well due to finding handwriting boring, finds difficulty with the visual perceptual and visual motor skills necessary to orient and place the words on the line, or because of decreased strength making it hard to apply the right amount of pressure, an Occupational Therapist can determine strategies to make it easier for your child to enjoy handwriting!
By: Shelby Godwin, COTA/L, AC